History
A 12 year old, female spayed American Shorthair cat, presented to Animal Imaging for an abdominal ultrasound after increased liver enzymes were noted on recheck bloodwork. Incidentally, the patient has a history of hyperthyroidism and was also scheduled for I-131 treatment pending results of the ultrasound. The patient also has a history of recent pancreatitis and a suspected urinary tract infection. The patient had been placed on antibiotics twice, and both times the owners noted significant improvement, then recrudescence of signs following cessation of antibiotics.
Recently, the owner reported that the patient was vomiting the methimazole pills and was anorexic. Bloodwork after starting medication showed changes in liver enzyme levels AST 175 IU/L (N: 15-100 IU/L), ALT 289 IUL (N: 10-100 IU/L), mildly elevated total bilirubin 0.5 md/dL (N: 0.1-0.4), and mildly decreased triglycerides 22 mg/dL (N:25-160). A urinalysis was also performed and showed a urine specific gravity of greater than 1.050 and a measure of urine protein level was 100+. An abdominal ultrasound performed by the boarded internist showed an unremarkable liver and a pancreas that appeared distended at the left limb. The patient was then referred to Animal Imaging for a secondary abdominal ultrasound and I-131 treatment.
Image Findings
Thoracic and Abdominal Radiographs
- Radiographs of the chest and abdomen were taken as part of the protocol for the thyroid scan and showed changes consistent with age and hyperthyroid disease (compensated cardiomyopathy)
- Abdominal films were fairly unremarkable
-
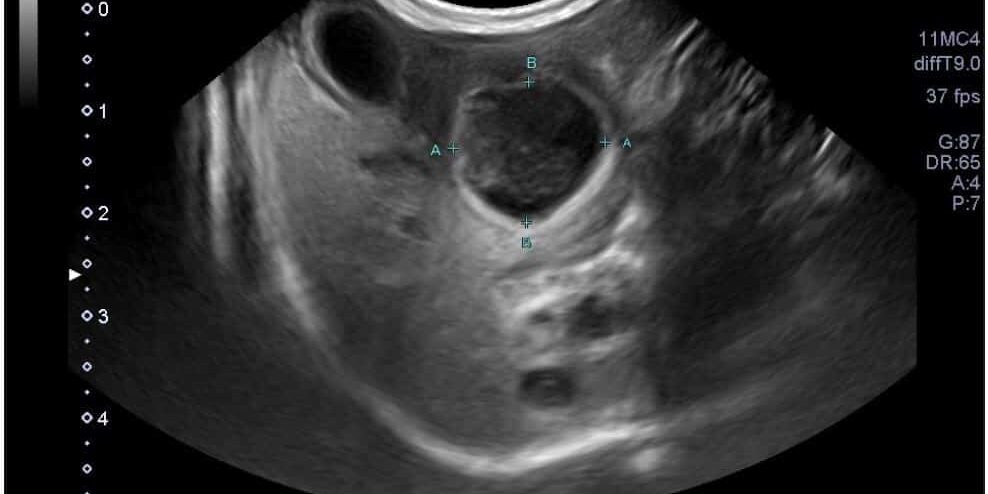
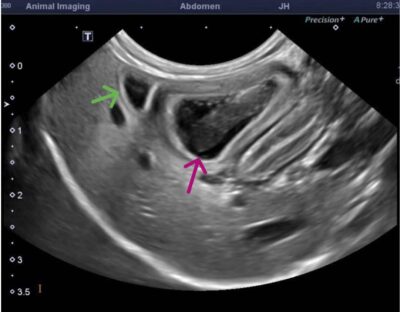
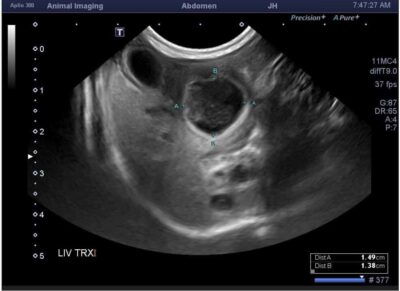
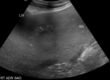
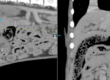
- A large (3.4cm L x 1.5cm W x 1.4cm H), ovoid, heterogeneously hypo- and anechoic structure with hyperechoic walls and echogenic swirling non-shadowing material centrally was noted at the right and mid liver adjacent to the very small gall bladder and cranial to the stomach. This structure was suspected to be a cavitated mass, abscess, or a duplicate gallbladder containing a large amount of echogenic material.
- The liver appeared diffusely and mildly hyperechoic, with decreased conspicuity of portal vein vascular walls.
- The left limb of the pancreas appeared enlarged and hypoechoic with mildly irregular margins.
Additional Diagnostics
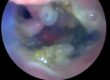
Fine needle aspirates were acquired of the liver lesion by Animal Imaging at the time of the ultrasound and submitted for cytology and culture. Purulent debris was obtained. Cytological results were consistent with neutrophilic inflammation (cholangiohepatitis) with no cytological evidence of neoplasia evident.
Comments
Ultrasonography was important in this case by identifying the structural changes within the liver that were not appreciated at the time the first ultrasound was performed. The gall bladder was quite small and easily missed on initial scan with the larger lesion appearing like a gallbladder. The fine needle aspirate and cytology performed provided additional data to confirm cellular changes due to inflammation and rule out a mass.
The enlargement of this patient’s heart could be associated with concurrent heart disease or a consequence of hyperthyroidism. An echocardiogram of the heart would be a possible next step if the patient was not already diagnosed with hyperthyroidism. Following a course of antimicrobial therapy with the referring veterinarian, the patient underwent I-131 treatment without further issue.